For Key and Descriptive Flexfields you might need to create Value Sets for restricting values user can enter.
People who are from EBS background knows about this. In EBS you can create value sets for Concurrent Program Parameters also. But here in Fusion Apps you create value sets only for flexfield segments.
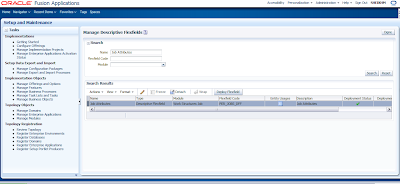
So let's get into the details. We create value sets through Manage Value Sets task from FSM [Navigator -> Tools(Setup and Maintenance)]
Once you go the task this is what you will see
You can search existing value sets and edit or you can create a new one. So for this exercise let us create some value sets. Click on the Actions -> Create or directly click on the create sign
The field elements are almost same as EBS. Let us see what are all the validation types available in Fusion Apps.
The following types of validation are available for value sets.
- Format Only, where end users enter data rather than selecting values from a list
- Independent, a list of values consisting of valid values you specify
- Dependent, a list of values where a valid value derives from the independent value of another segment
- Subset, where the list of values is a subset of the values in an existing independent value set
- Table, where the values derive from a column in an application table and the list of values is limited by a WHERE clause
In the above example I created XXCUSTOM_COMPANY value set with Validation Type Independent and Value Data Type Character in General Ledger Module. Once you have specified the details click on Save and Close. It will go back to the Manage Value Sets screen. Search the value set and click on Manage Values to enter the values
Select the row and click on Manage Values button or Select Manage Values from Actions menu.
This is what you see in the Manage Values screen. You can search existing Values or can create new ones. Select Actions -> Create
In the Create Value sreen specify the Value, Description and optionally specify the Start Date, End Date and Sort Order.
Click and Save and Close. In this way you can create all the required values.
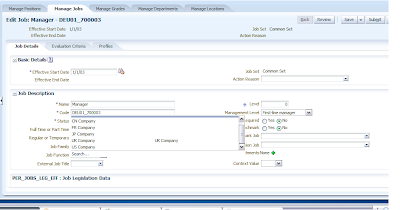
Let's associate this Value Set in one of the segments in the Descriptive Flexfield I setup in the previous post.
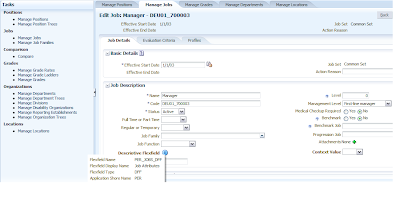
So Search the Manage Descriptive Flexfields in FSM and Click on Go to Task. In the following screen search Job Attributes DFF and then click on Actions -->Edit
This is what you will see in the following screen. Let us associate our Value Set XXCUSTOM_COMPANY with DFF Global Segment External Job Title. Click on Actions --> Edit
In the Edit Segment Screen select the Combobox and then select Search
Search XXCUSTOM_COMPANY and then select it and then then click Ok. In the Edit Segments screen click Save and Close. And then in Edit Descriptive Flexfields screen click Save and Close again.Then finally in Manage Descriptive Flexfields screen select the DFF and click on Deploy Flexfield.
Now let's see whether our value set is working or not. Go to Navigator --> Workforce Management --> Workforce Structures
Go To Manage Jobs Tab and search or Create a Job and then Click on External Job Title Combobox. The list will show you the values you defined in the value sets
This screen confirms the same.
Security
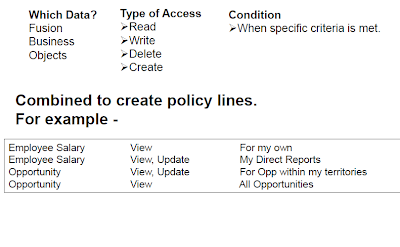
Value set security only works in conjunction with usage within flexfield segments. If a value set is used standalone, meaning outside a flexfield, value set security is not applied, but Oracle Fusion data security is enforced.
You can specify that data security be applied to the values in flexfield segments that use a value set. Based on the roles provisioned to users, data security policies determine which values of the flexfield segment end users can view or modify.
Value set security applies at the value set level. If a value set is secured, every usage of it in any flexfield is secured. It is not possible to disable security for individual usages of the same value set.
Value set security applies to independent, dependent or table-validated value sets.
Value set security applies mainly when data is being created or updated, and to key flexfield combinations tables for query purposes. Value set security does not determine which descriptive flexfield data is shown upon querying.
Security conditions defined on value sets will always use table aliases. When filters are used, table aliases are always used by default. When predicates are defined for data security conditions, make sure that the predicates will also use table aliases.
For key flexfields, the attributes in the view object that correspond to the code combination ID (CCID), structure instance number (SIN) and data set number (DSN) cannot be transient. They must exist in the database table. For key flexfields, the SIN segment is the discriminator attribute, and the CCID segment is the common attribute.
Value Sets for Context Segments
When assigning a value set to a context segment, you can only use table-validated or independent value sets. The data type must be character and the maximum length of the values being stored must not be larger than column length of the context.
Cheers......